What are telomeres?
Telomeres are specific DNA-protein structures found at the ends of each chromosome that protect the genome from nucleic acid degradation, unwanted recombination, repair, and interchromosomal fusions. Therefore, telomeres play a crucial role in preserving the information in our genome.
As a normal cellular process, a small portion of telomeric DNA is lost with each cell division. When telomere length reaches a critical limit, cells undergo senescence and apoptosis. Therefore, telomere length can serve as a biological clock that determines the lifespan of cells and organisms. Certain medications associated with specific lifestyles may accelerate telomere shortening by causing DNA damage at telomeres in general or more specifically, and may therefore affect an individual’s health and longevity.
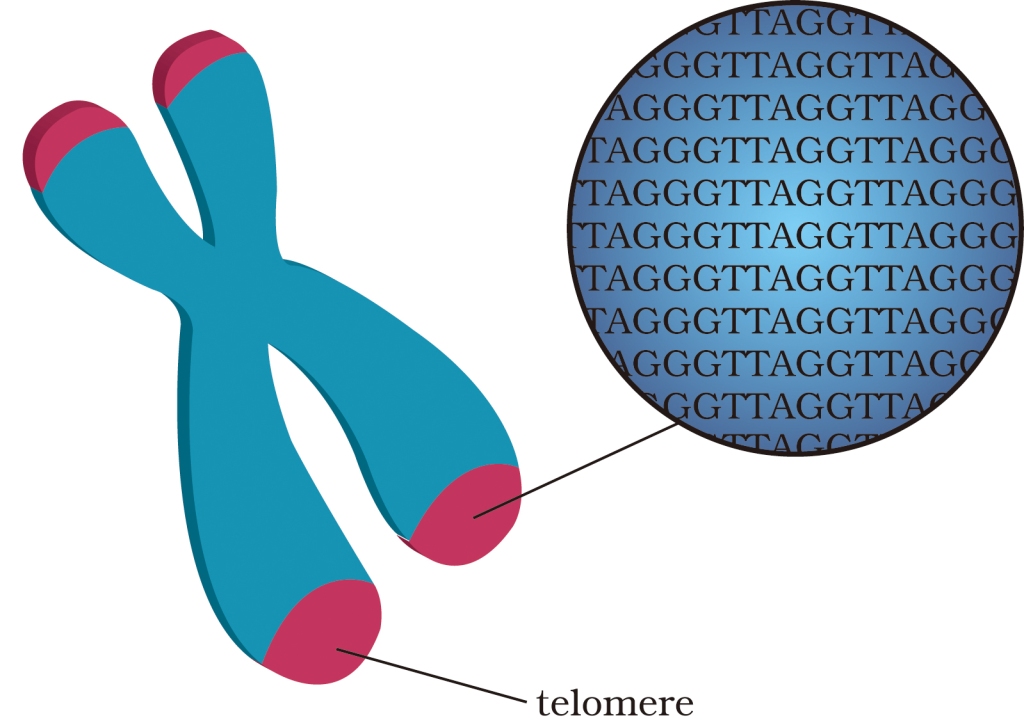
- Telomeres are special structures at the ends of chromosomes.
- It consists of repeated DNA of the same sequence,which is called “TTAGGG" in humans.
- There are 3000 repeats up to 15000 base pairs length.
What is Telomerase?
Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein complex composed of RNA and protein. It belongs to reverse transcriptase and is closely related to the regulation mechanism of telomeres.
Human telomerase subunit genes have been copied, namely telomerase RNA (hTR), telomerase-binding protein (hTP1), and telomerase activity catalytic unit (hTERT). It uses its own RNA as a template for telomere DNA replication, synthesizes a DNA sequence rich in deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP), adds it to the end of the chromosome and binds to telomere proteins, thereby stabilizing the structure of the chromosome .
- In normal human cells, the activity of telomerase is quite tightly regulated.Only in hematopoietic cells, stem cells and germ cells, which must be constantly dividing and replicating, can active telomerase be detected.
- When cells mature, they must be responsible for the needs of various tissues in the body, so the activity of telomerase will gradually disappear.
- Telomerase plays an important role in maintaining telomere stability, genome integrity, long-term cell activity, and potential for continued proliferation.
- The existence of telomerase is to make up for the defects of the DNA replication mechanism, that is, by extending the telomere repair, it can prevent the telomeres from being lost due to cell division, and increase the number of cell division and replication.